What are the common failure modes of single-row ball slewing bearings and how can they be prevented?
 2024.09.06
2024.09.06
 Industry news
Industry news
Single-row ball slewing bearings, renowned for their smooth rotational capabilities and robust load-bearing capacity, are pivotal in various applications ranging from construction machinery to wind power generation and medical equipment. Despite their advanced design and high-quality materials, these bearings are not immune to failure. Understanding the common failure modes and their prevention is crucial for ensuring their longevity and optimal performance.
One of the most frequent failure modes of single-row ball slewing bearings is fatigue failure. This occurs when the bearing is subjected to repetitive stress cycles that exceed its design limits, leading to surface cracks and eventual material degradation. Fatigue failure can be exacerbated by improper load distribution, misalignment, or overloading. To prevent this, it is essential to ensure that the bearing is correctly installed and aligned, and to avoid exceeding the specified load limits. Regular inspections can help identify signs of wear or stress early, allowing for timely maintenance or replacement.
Another common issue is lubrication failure, which can result in increased friction, overheating, and accelerated wear. Lubrication is critical for minimizing friction and reducing wear between the steel balls and the raceways. Insufficient or improper lubrication can lead to dry contact, causing significant damage. To mitigate this risk, it is important to use the correct type and amount of lubricant as specified by the manufacturer and to perform regular checks to ensure that the lubrication system is functioning correctly. Additionally, bearings should be monitored for any signs of leakage or contamination that might compromise lubrication effectiveness.
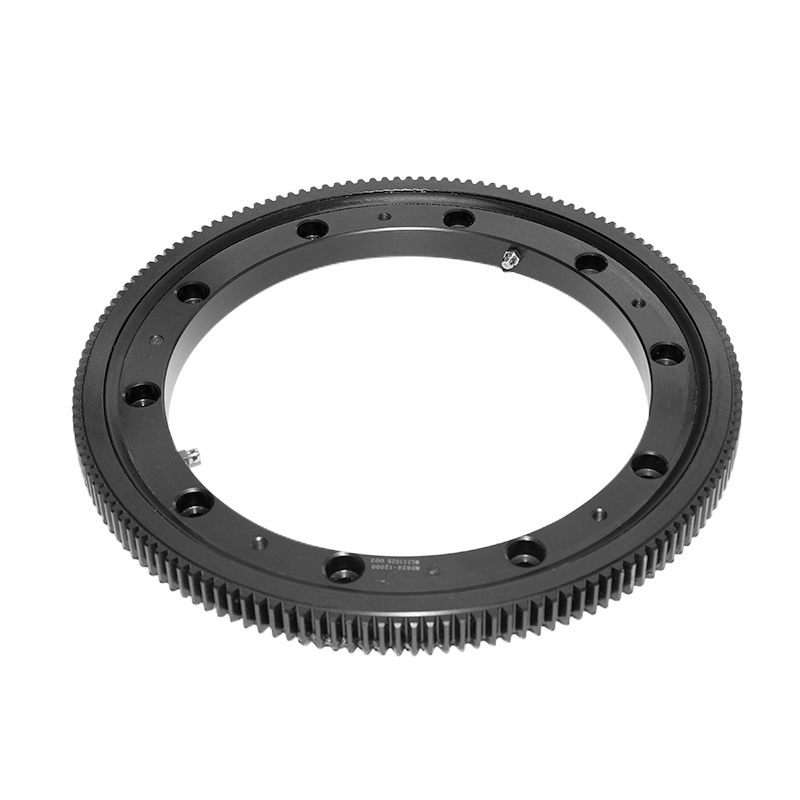
Contamination is another major concern for single-row ball slewing bearings. Dust, dirt, or moisture ingress can cause abrasive wear and corrosion, leading to reduced performance and a shorter service life. Bearings equipped with seals are designed to protect against such contamination, but if these seals become damaged or degraded, they may not provide adequate protection. Regular inspection and maintenance of the seals, as well as ensuring that the bearing is operating in a clean environment, are crucial for preventing contamination-related issues.
Misalignment is a failure mode where the bearing’s raceways are not properly aligned with each other, causing uneven load distribution and excessive wear. This can result from improper installation or deformation of the supporting structures. To prevent misalignment, it is important to ensure precise installation and to regularly check for alignment during operation. Any signs of misalignment should be corrected immediately to avoid further damage.
Lastly, excessive temperature can adversely affect the performance and lifespan of single-row ball slewing bearings. High temperatures can lead to lubricant breakdown, increased wear, and thermal expansion, which may distort the bearing’s components. Proper temperature management, including monitoring and controlling the operating environment and using appropriate lubricants that can withstand high temperatures, is essential for maintaining bearing performance.
While single-row ball slewing bearings are engineered for high performance and durability, they are susceptible to various failure modes such as fatigue failure, lubrication issues, contamination, misalignment, and excessive temperature. By adhering to proper installation procedures, ensuring regular maintenance, using the correct lubricants, protecting against contamination, and managing operating conditions, one can significantly reduce the risk of these failures and extend the bearing’s operational life. Regular inspections and prompt corrective actions are key to preventing these issues and ensuring the reliable performance of single-row ball slewing bearings in their diverse applications.