What type of lubrication is recommended for single-row ball slewing bearings?
 2025.01.18
2025.01.18
 Industry news
Industry news
The type of lubrication recommended for single-row ball slewing bearings depends on various factors, including the operating conditions, load types, speed, and environmental conditions. However, there are some general guidelines and options commonly used for ensuring optimal performance and longevity:
1. Grease Lubrication
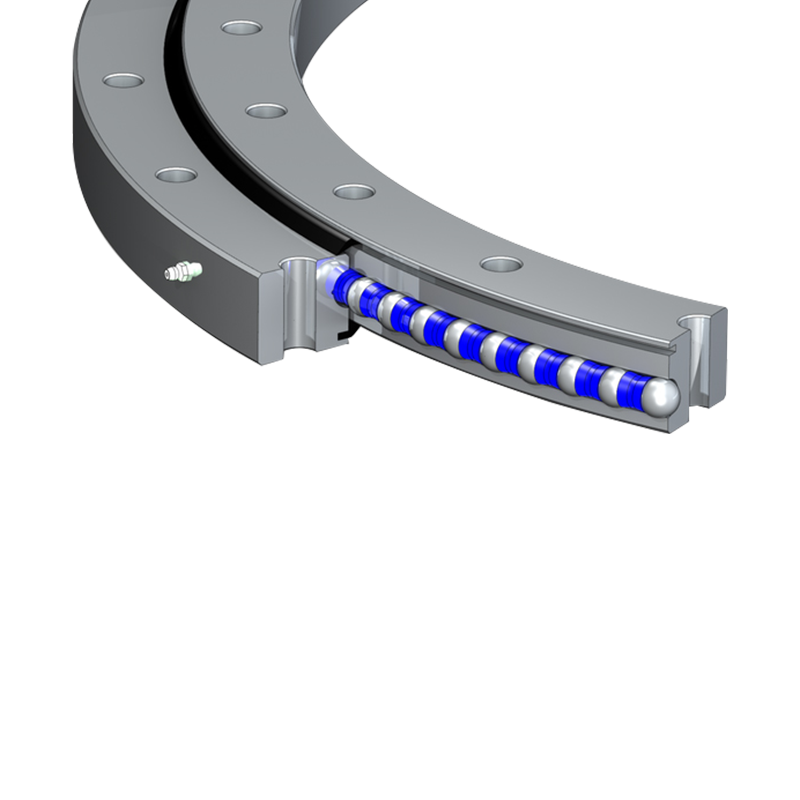
Grease is the most commonly used lubricant for single-row ball slewing bearings, especially in low to moderate-speed applications. It is preferred because it provides both lubrication and sealing properties. Some important points about grease lubrication include:
High-Quality Grease: A high-quality, multi-purpose grease with a good base oil viscosity and additives (such as EP additives for extreme pressure) is typically used. Lithium-based or lithium complex greases are common choices.
Consistency (NLGI Grade): The NLGI (National Lubricating Grease Institute) grade of the grease should be selected based on the operating temperature and the bearing’s operating conditions. For most slewing bearings, a grease with an NLGI grade of 2 (medium consistency) is standard, though some applications may require lighter or heavier grades.
Additives: Greases with anti-wear, anti-corrosion, and extreme pressure (EP) additives are beneficial in improving the bearing’s performance, especially under high-load or high-shock conditions.
2. Oil Lubrication
Oil lubrication is often used for high-speed applications or when greater cooling is needed. Oil can be applied through an automatic lubrication system or manually, depending on the application. Some important points about oil lubrication include:
Viscosity: The viscosity of the oil should be chosen based on the load, temperature, and speed of the bearing. For high-speed applications, lower viscosity oils are often used, while higher viscosity oils are required for high-load conditions.
Types of Oils: Mineral oils, synthetic oils, and semi-synthetic oils are commonly used. Synthetic oils are often preferred in extreme conditions (e.g., very high or low temperatures or heavy loads) due to their superior thermal stability and longer service life.
Additives: Similar to grease, oils may contain additives like anti-wear agents, corrosion inhibitors, and antioxidants to ensure longer bearing life, particularly in harsh operating conditions.
3. Lubrication Systems
The method of applying lubrication also plays a crucial role in maintaining the bearing’s performance:
Manual Lubrication: In some cases, lubrication is applied manually at regular intervals. This is common in applications where the bearings do not operate continuously or where automatic systems are not feasible.
Automatic Lubrication Systems: For continuous or high-duty-cycle operations, automated lubrication systems such as centralized grease or oil lubrication systems are used. These systems ensure that the bearings receive consistent lubrication without the need for manual intervention.
Oil Circulation Systems: For high-speed or high-temperature operations, a circulating oil system might be used to continuously supply fresh oil to the bearing and remove heat, ensuring proper lubrication and cooling.

4. Grease vs. Oil
Grease: Grease offers better sealing properties and is ideal for slow to moderate-speed applications. It also provides longer-lasting lubrication in conditions where oil might leak out or evaporate. However, grease may need to be replenished periodically, depending on the operating environment.
Oil: Oil provides better cooling, especially in high-speed applications, and can be used in systems where automatic lubrication or oil circulation is practical. However, it requires careful sealing to prevent leakage and maintain its effectiveness.
5. Lubrication Considerations Based on Operating Conditions
Temperature Range: For high temperatures (above 100°C or 212°F), synthetic greases or oils with high thermal stability should be used. At low temperatures, greases or oils with better pumpability and lower pour points are needed to prevent solidification.
Environmental Conditions: In outdoor or harsh conditions, such as heavy dust, moisture, or corrosive environments, greases with moisture-resistant and corrosion-inhibiting additives should be used. Special sealing systems may also be employed to protect the bearing from contaminants.
Speed and Load: For high-load or slow-speed applications, high-viscosity grease with EP additives is preferred. For high-speed operations, low-viscosity oils or lighter greases are recommended to reduce friction and heat generation.
6. Maintenance and Replenishment
Re-lubrication Intervals: Regular re-lubrication is important for maintaining the performance of single-row ball slewing bearings. The intervals depend on the operational conditions, such as load, speed, and environmental factors. Automatic lubrication systems often help maintain optimal grease levels and reduce the risk of over- or under-lubrication.
Grease Purging: In some applications, grease purging is used to remove old, contaminated grease and replace it with fresh grease. This helps prevent bearing wear and ensures that the lubrication remains effective.